India’s banking sector stands at a defining moment in its modern history. With the economy expanding and policy frameworks evolving, the financial system is entering an era of structural transformation — one where liquidity, regulation, and digital innovation are converging to shape a stronger, more resilient ecosystem.
As of April 2025, total bank deposits in India stood at ₹2,33,56,673.93 crore (approximately $2.75 trillion USD), while bank credit reached ₹1,86,56,448 crore (around $2.2 trillion USD). These are not just large numbers — they represent the sheer scale of India’s financial intermediation capacity and the depth of trust that households and businesses place in the formal banking system.
Amid this growth, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has played a critical role in ensuring stability. Its decision in June 2025 to reduce the Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) by 25 basis points reflects a proactive stance toward maintaining liquidity, stimulating credit, and supporting broader economic expansion.
The story of India’s banking reinvention can be understood through four powerful forces — liquidity and capital strength, regulatory discipline, digital transformation, and risk resilience.
Liquidity and Capital Strength: The Backbone of Stability
The foundation of any strong banking system lies in its ability to remain liquid and well-capitalized. India’s banks, both public and private, have maintained capital adequacy ratios (CAR) comfortably above the regulatory minimum prescribed by the Basel III norms — a testament to their sound financial management and policy prudence.
The RBI’s liquidity management tools, including its recent CRR cut, are aimed at injecting liquidity into the banking system, thereby lowering the cost of funds and encouraging credit expansion. These interventions enable banks to lend more freely to businesses, consumers, and infrastructure projects — reinforcing the virtuous cycle of growth and stability.
This combination of ample liquidity and strong capitalization has allowed Indian banks to remain resilient even amid global financial uncertainty, currency volatility, and tightening liquidity elsewhere in the world.
Regulatory Evolution: Strengthening Robustness and Transparency
Over the last few years, the RBI’s regulatory architecture has been steadily upgraded to align Indian banks with global best practices. A key step in this journey is the introduction of the Expected Credit Loss (ECL) framework — a shift from a reactive, incurred-loss model to a forward-looking risk assessment approach.
Under ECL norms, banks are required to provision for potential losses in advance, based on estimated credit deterioration. This enhances transparency, strengthens balance sheets, and reduces the element of surprise in bad loan recognition — an area where Indian banking once faced significant challenges.
Equally critical is the RBI’s tightening of digital banking guidelines, ensuring that innovation in areas like online lending, digital wallets, and neobanking is balanced with robust cybersecurity and governance standards. Together, these measures create a regulatory environment that is not only stable but also adaptive to the fast-changing nature of finance.
Digital Transformation: Fueling Inclusion and Efficiency
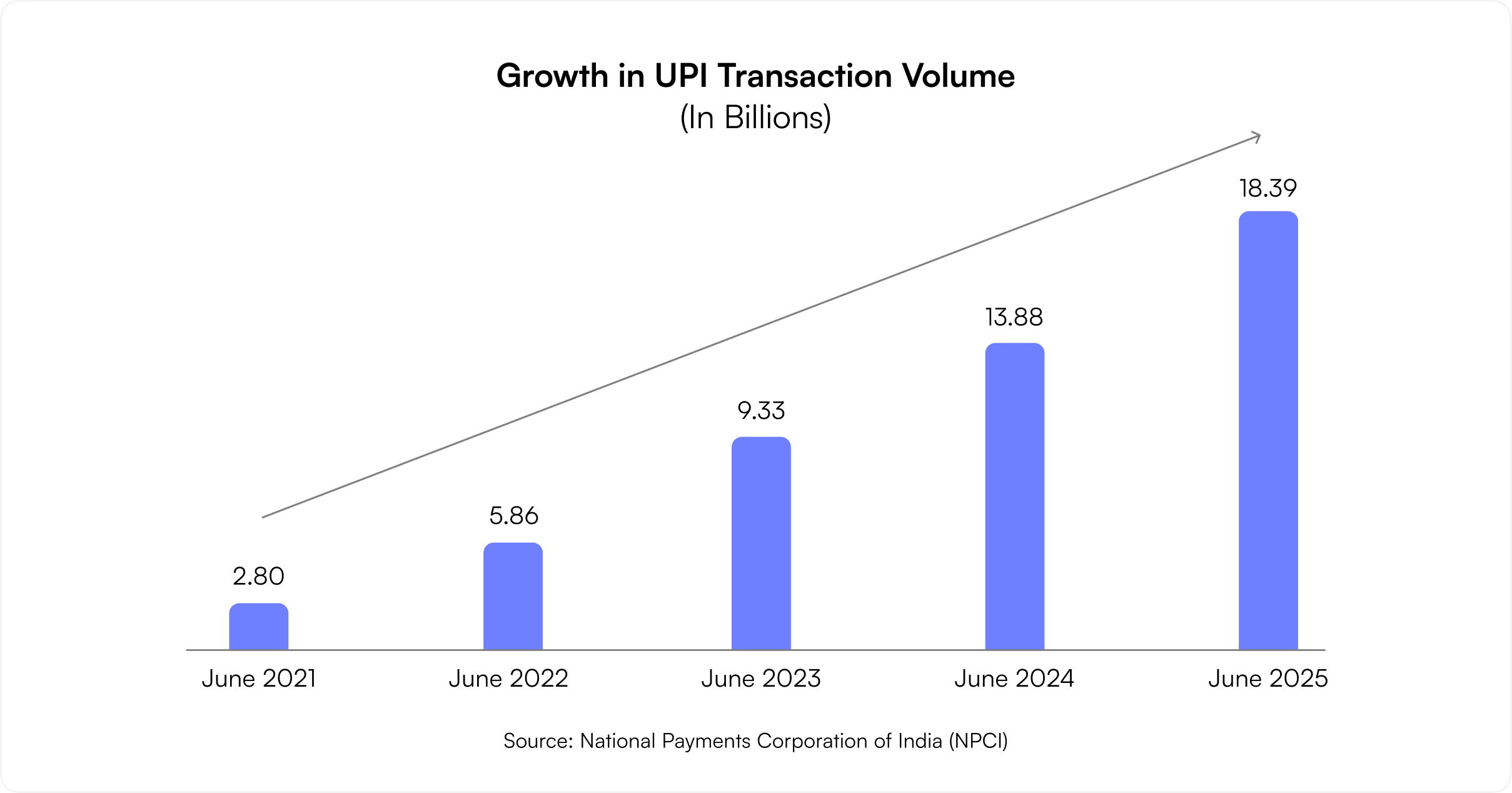
Few countries have witnessed a digital payments revolution as dramatic as India’s. The Unified Payments Interface (UPI) continues to redefine how money moves — seamlessly, instantly, and inclusively.
By June 2025, UPI processed transactions worth ₹24.03 lakh crore (approximately $240 billion USD), underscoring its unmatched reach and reliability. The framework has effectively turned every smartphone into a bank branch, enabling financial participation for millions who were previously outside the formal system.
Complementing UPI’s success are initiatives like Digital Banking Units (DBUs) and the government’s Digital India mission, which together are expanding access to credit, savings, and investment products across the country — from urban centers to the most remote villages.
This digital shift is not just about convenience; it’s about efficiency, transparency, and empowerment, bringing India closer to a truly inclusive financial ecosystem.
Risk Management and Resilience: The New Core Competency
In an era of volatility — whether from global monetary shifts, market cycles, or credit risks — India’s banks are focusing more than ever on predictive risk management.
The adoption of the ECL model allows banks to assess loan portfolios more dynamically, identifying early signs of stress and provisioning proactively. This represents a paradigm shift from firefighting to foresight — ensuring that shocks are absorbed before they escalate.
The RBI’s ongoing supervision, stress tests, and periodic reviews further ensure that systemic risks are identified early. This continuous adaptation has strengthened confidence among depositors, investors, and global observers alike, positioning India’s banking sector as one of the most resilient in emerging markets.
A Future-Oriented Financial Ecosystem
The transformation unfolding in India’s banking sector is not episodic — it’s structural. The interplay between liquidity support, regulatory foresight, and digital modernization is creating a financial architecture built for the next decade.
With sound capital buffers, progressive policy reforms, and a tech-driven expansion of inclusion, India’s banks are well-positioned to power the country’s economic ambitions while safeguarding stability.
As the sector evolves, its greatest strength will lie not just in numbers but in its capacity to adapt — prudently, digitally, and sustainably.

Team Axe
Markets move on stories as much as on numbers. Team Axe looks at both — the data underneath and the narrative on top — to show which themes are durable and which are just this week’s excitement.