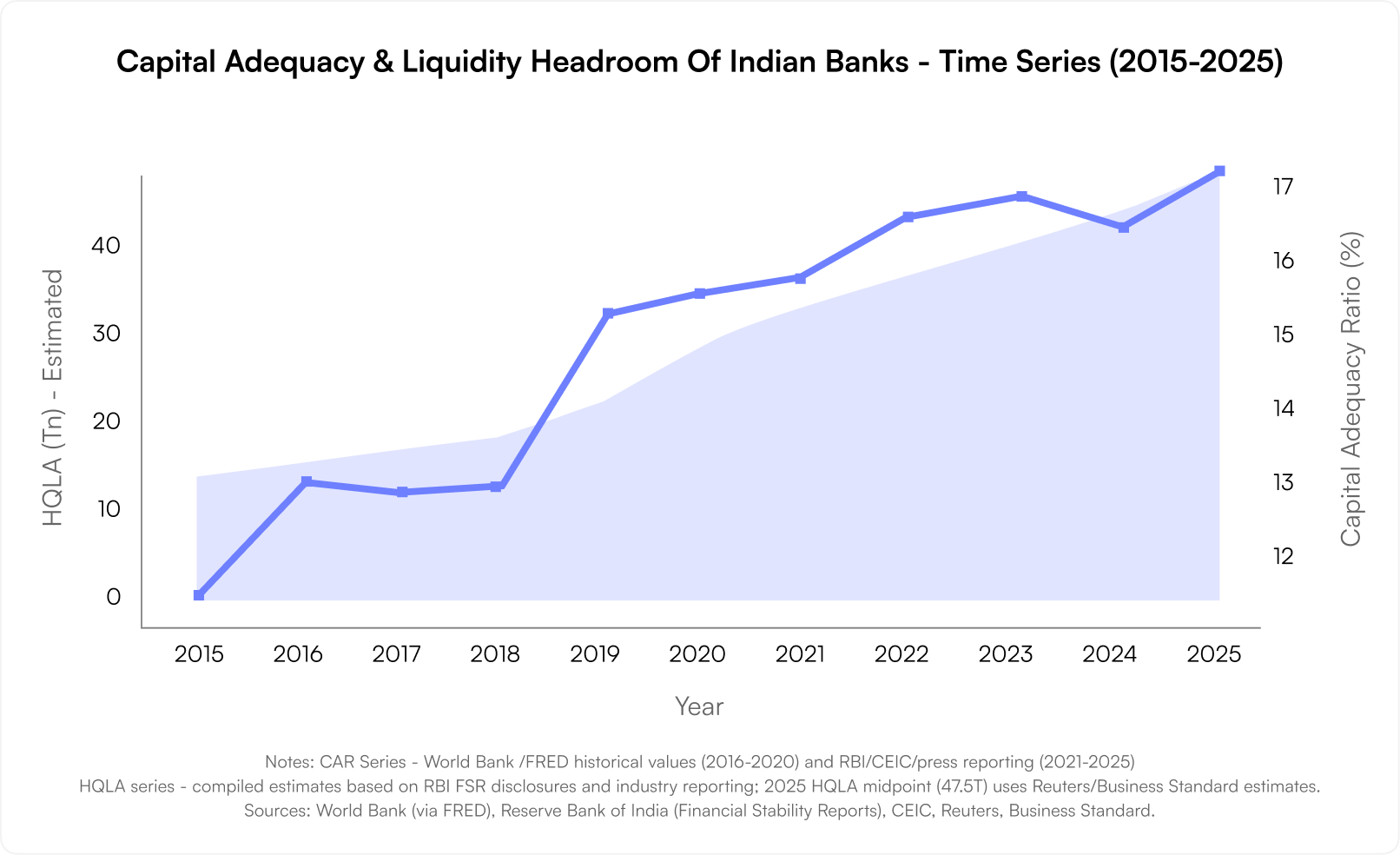
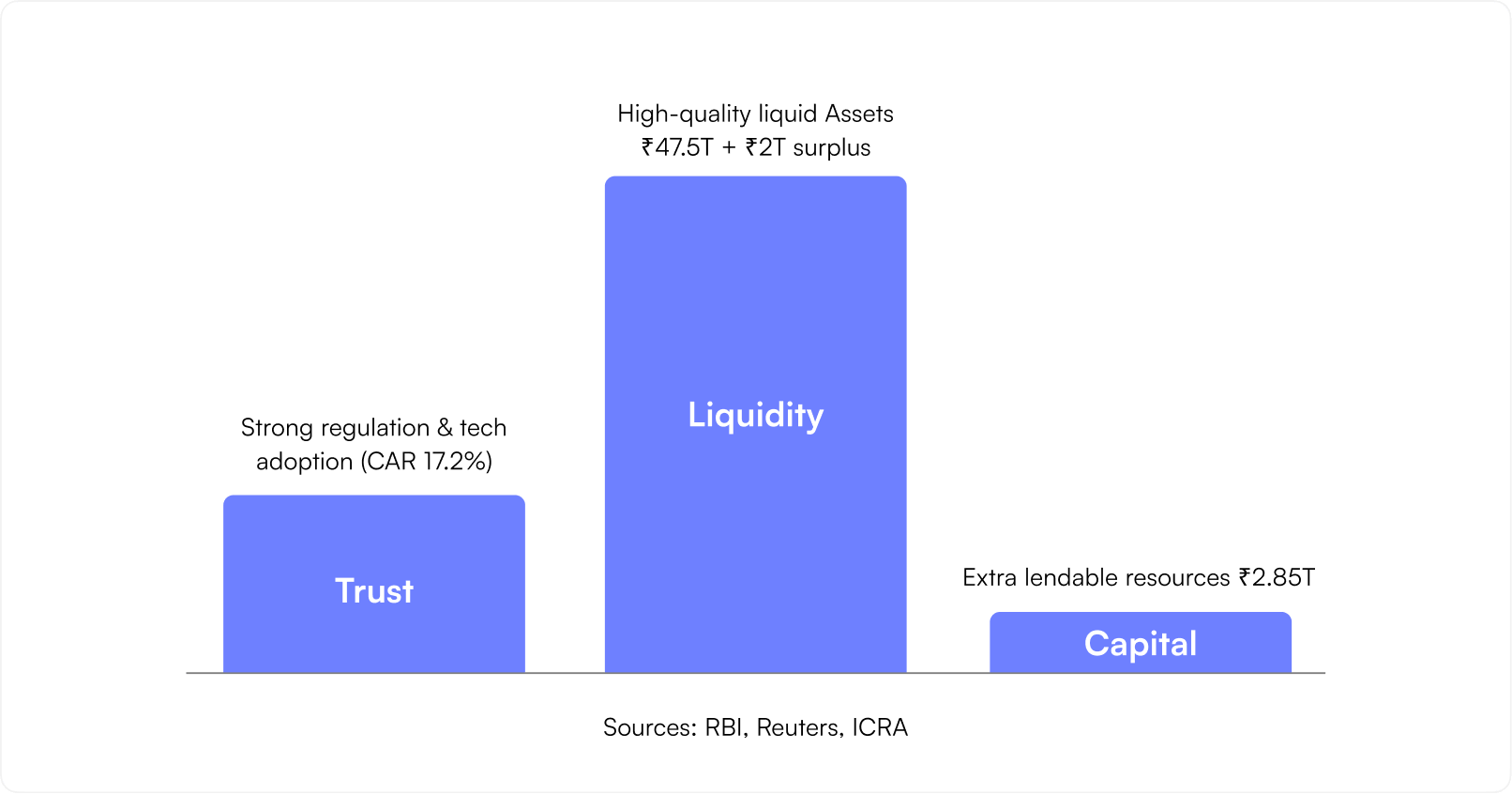
In 2025, India’s banking sector stands as a story of resilience, reinvention, and renewed confidence. With a capital adequacy ratio (CAR) of 17.2% as of March 2025, Indian banks are not just stable — they’re thriving, outpacing the Basel III global minimum requirement of 8%.
This robust capital foundation, coupled with proactive regulation and rapid digital adoption, has transformed India’s banking system into one of the most trusted pillars of the country’s economic architecture.
At its heart, however, the banking system runs on three currencies that go beyond money — trust, liquidity, and capital. Together, they form the confidence economy that powers India’s financial future.
Trust as the Cornerstone of Banking
In banking, numbers tell only half the story — the other half is trust. India’s financial ecosystem continues to reinforce this trust through transparency, accountability, and technology. The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has deepened its oversight mechanisms and compliance frameworks, ensuring that banks maintain the highest governance standards. Alongside this, the adoption of AI, data analytics, and blockchain has brought unprecedented visibility and precision to operations.
This intersection of regulation and innovation is redefining reliability — helping depositors, investors, and institutions believe that the system is not only safe but smarter than ever before.
Liquidity: The Silent Driver of Growth
While trust anchors the system, liquidity fuels its movement.
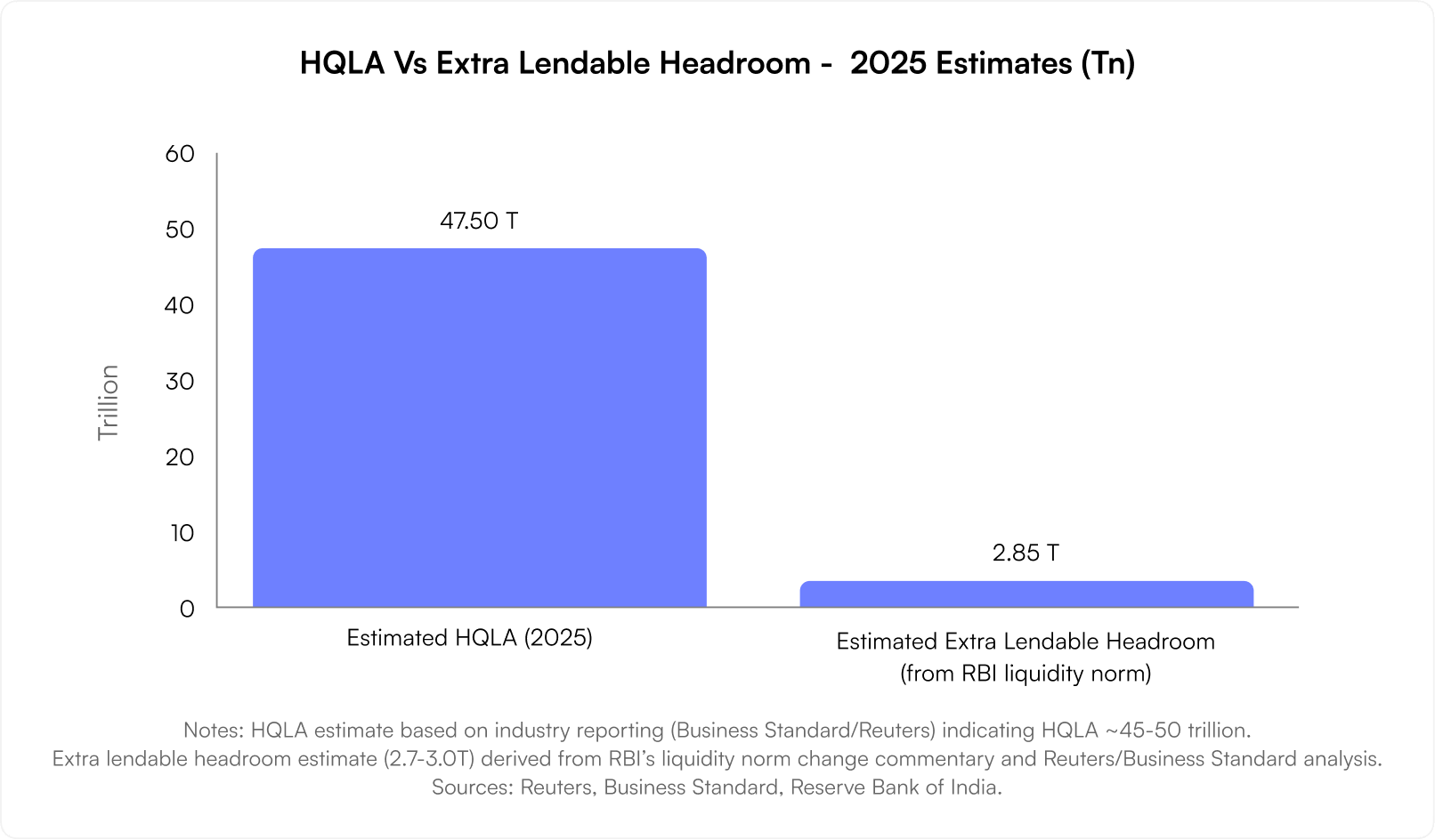
As of 2025, India’s banking system holds a formidable ₹45–50 trillion in High-Quality Liquid Assets (HQLA). With the RBI’s latest liquidity norms, an additional ₹2.7–3 trillion could be unlocked for lending.
Such abundant liquidity acts as oxygen for growth — enabling banks to finance credit demand, businesses to expand, and consumers to spend with confidence. In essence, liquidity ensures that the economy keeps breathing, even in volatile times.
Capital Adequacy: The Guardian of Stability
A CAR of 17.2% isn’t just a statistic — it’s a symbol of preparedness. This high buffer allows Indian banks to absorb potential shocks while maintaining lending activity through uncertain cycles.
That said, the journey ahead isn’t without challenges. Rising delinquencies in retail loans and microfinance segments have started testing the sector’s resilience. The focus, therefore, is shifting towards smarter risk management, AI-led credit monitoring, and balanced portfolio diversification — not as defensive tactics, but as proactive safeguards of stability.
Digital Transformation: Banking Beyond Boundaries
If capital defines strength and liquidity defines motion, digital transformation defines reach. In August 2025, UPI processed over 20 billion transactions worth ₹24.85 trillion, an unprecedented figure that underlines India’s lead in digital payments.
But the evolution doesn’t stop at payments. The integration of UPI with AI chat interfaces is making banking conversational — allowing users to transact, inquire, and invest through natural language commands.
This shift marks the transition from digital convenience to intelligent financial ecosystems, where access meets personalization.
Mergers & Acquisitions: Building Scale and Synergy
Consolidation has emerged as a key theme in India’s banking narrative. In the first half of 2025 alone, the sector recorded $50 billion in merger and acquisition deals, with 10 transactions exceeding $1 billion each.
Among the most notable moves is Emirates NBD’s advanced discussions to acquire up to a 25% stake in RBL Bank — a deal that signals international confidence in India’s banking potential. These transactions reflect not just scale-building, but also strategic alignment — where capital, technology, and customer ecosystems converge to create stronger, more competitive institutions.
Conclusion: The Confidence Economy in Motion
India’s banking sector in 2025 stands on a tripod of trust, liquidity, and capital — the true currencies that underpin its strength.
As digital innovation deepens, global partnerships expand, and regulatory foresight continues to guide the system, India’s banks are no longer just financial intermediaries — they are architects of economic confidence.
The future of Indian banking will not merely be measured in profits or balance sheets, but in its ability to inspire trust, sustain liquidity, and protect capital — the timeless foundations of a confident economy.

Dikshant Patel
Focused on research and financial analysis, I explore how markets respond to changing economic and policy environments. My interest lies in connecting the dots between data, sentiment, and long-term trends that shape investor outcomes. Through a structured and objective approach, I aim to make financial discussions more accessible while maintaining analytical depth and precision.